Mini Review
Fungi present in home and their impact on human health-A short review

Mariusz Dyląg*
Department of Genetics, Institute of Genetics and Microbiology, University of Wroclaw, Przybyszewskiego Street 63/77, 51 -148 Wroclaw, Poland
*Address for Correspondence: Dr. Mariusz Dyląg, Department of Genetics, Institute of Genetics and Microbiology, University of Wroclaw, Przybyszewskiego Street 63/77, 51 -148 Wroclaw, Poland, Email: [email protected]
Dates: Submitted: 19 April 2017; Approved: 05 June 2017; Published: 06 June 2017
How to cite this article: Dyląg M. Fungi present in home and their impact on human health-A short review. Insights Biol Med. 2017; 1: 016-025. DOI: 10.29328/journal.ibm.1001003
Copyright License: © 2017 Shengelia R, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
It is estimated that even up to 30% of buildings worldwide may be the subject of complaints connected with the quality of indoor air. Potential sources of air pollution can be both organic and inorganic particles. This article focuses on biological air pollutants from living and dead biological sources, especially those connected with fungi. Fungi found in the indoor air of domestic dwellings in a large extent are similar in their species composition to those found on the outside of the building. Microorganisms enters into the buildings during the airing of rooms or through the different slots and can develop on the surfaces of various materials. Intensively develops in a poorly ventilated, damp and dusty environments. For this reason the exposure to the indoor air pollution might be stranger for inhabitants than the expose to the impurities of the outdoor air. Presence of fungi in domestic dwellings can be very danger because of most often is associated with allergic reactions, mycotoxins, volatile organic compounds or even with fungal infections.
INTRODUCTION
People spend approximately 90% of their free time inside their dwellings. Although it is hard to believe the exposure to the indoor air pollution might be stranger than the expose to the impurities of the outdoor air [1,2]. Only in the years 1978-2016 issues related to indoor air quality was devoted fourteen international conferences. Released in 1984 by the WHO (World Health Organization) report, up to 30% of buildings worldwide are suggested to be the subject of complaints connected with the quality of indoor air [3-5]. Over the past years this problem has not decreased or even intensified, as can be inferred from the latest WHO report-WHO guidelines for indoor air quality: dampness and mold. It is estimated that indoor dampness affect 10-50% of indoor environments in Europe, and in the other highly developed countries [6]. Increasingly, there are reports of respiratory symptoms associated with staying in homes with humidity problems and the presence of microorganisms on various building materials [7]. Here we also points out that poor indoor air quality can cause occupational diseases [8,9]. The quantity and type of pollutants suspended in the air determine the quality of this air. Potential sources of air pollution can be both organic and inorganic particles. This article focuses on biological air pollutants as natural pollutants from living and dead biological sources. When thinking about biological factors, microbes are deserving of attention. Microorganisms enter to the interior of the building from the outside, but what’s worth emphasizing is that inside there are major sources for development [10,11]. Indoor microorganisms are present in the air as so called bioaerosol, they settle on different surfaces, can develop in layers of condensed steam on the walls and windows, on food remains, under carpets and on any other damp material. Particularly good environment for the development of many microorganisms is home dust [12,13]. A large number of microorganisms, and in particular mold fungi, often colonize air filters of air -conditioning equipment. Then it will be the direct source of air pollution. The cases of colonization of air filters by molds were also found in hospitals [14]. For this reason, it is understandable that the species of fungus isolated from the indoor air are at least in 50% identical with isolated from different materials, dust, or from the surface of the walls of these rooms [15,16]. Spores or conidia and other structures of fungi enter the human body in various ways: per os, per nasal or per cutaneum [10,17,18].
FUNGI AND ALLERGIC REACTIONS
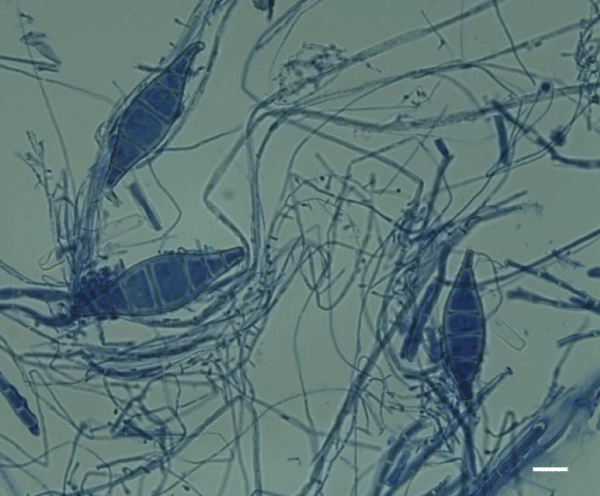
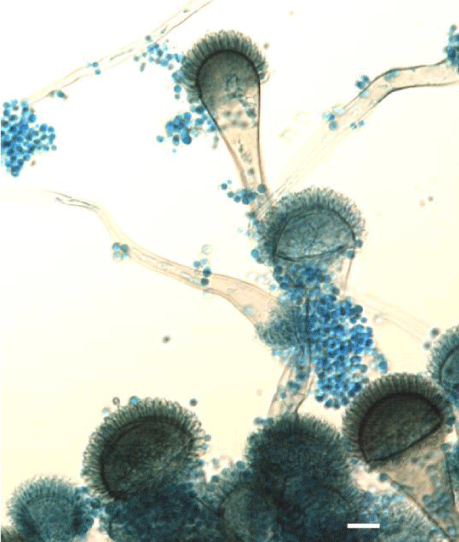
Presence of fungi in domestic dwellings often is associated with allergic reactions [10,19]. The ability to induce inflammatory reactions by fungi depends in a large degree on the growth environment and in particular on the type of substrate [18]. Allergy to fungi may be manifested by: bronchial asthma, rhinitis, conjunctivitis, urticaria, or atopic dermatitis. Fungi, depending on the species, are capable to induce all the four types of hypersensitivity reactions [20,21]. Among all the described types of allergic reactions caused by fungi to the most common belongs hypersensitivity of the type I - immediate reaction, IgE-dependent. This type of immune response is also called anaphylactic and clinically is manifested as asthma, rhinitis, sinusitis, urticaria, swollen vascular or obturation of bronchi. In this case fungal allergens induce IgE production which opsonised mast cells and basophiles [20,22]. Usually symptoms appear after 10-30 minutes after contact with allergen. Type II reactions are less frequent. Fungal antigen capable to induce this type of reaction is most commonly mannan, mainly found in cell walls of the genus Aspergillus and Candida [23]. These are cytotoxic reactions -dependent mainly from IgG and IgM antibodies or cells such cytotoxic lymphocytes, natural killer (NK) cells, or activated macrophages directed toward antigen which is embedded on blood cells or constitutes a component of cell membrane [23]. With the type III sensitization to fungal antigens, we meet in the case of allergic alveolitis and bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA-allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis) [24]. This type of allergic reaction is usually associated with immune complexes consisting of fungal antigens and antibodies. Such complexes are formed by the presence of small amounts of fungus in the body (in the case of APBA) or repeated exposure to small conidia such these formed by Aspergillus fumigatus (Figure 1) which achieved only 2-3.5 microns [25,26]. Such structures easily invade to the lower respiratory tract [25]. Clinical symptoms of the hypersensitivity reactions type III occur approximately 4-6 hours after exposure to the allergen. Finally, type IV of hypersensitivity reaction develops 24-48 hours after the contact of antigen with Th1 (CD4+) sensitized lymphocyte. Here the antigen can be some fungal cell structures or haptens produced by some fungi or, as recently was described may be connected with Archaea species [27]. Clinically, type IV of hypersensitivity reactions may be manifested by contact dermatitis or urticaria. Also described are granulomatous cases with characteristic inflammatory infiltrates [28].
Figure 1: Aspergillus fumigatus Fresen-etiologic agent of pulmonary aspergillosis as well different types of hypersensitivity reactions. Scale bar 10 μm.
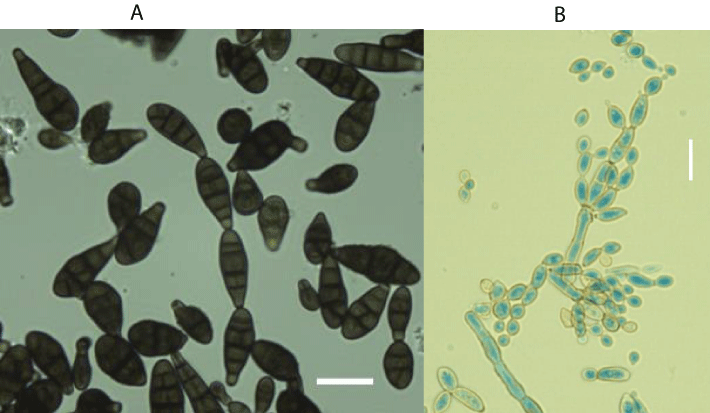
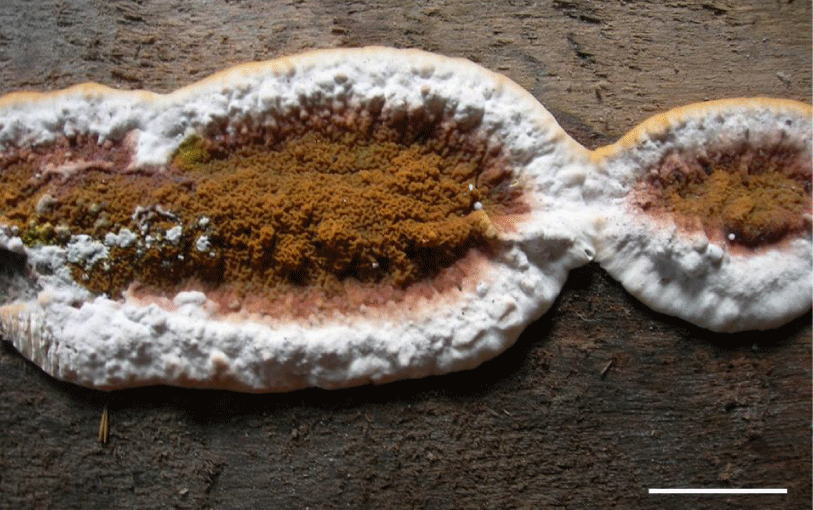
Fungal spores in some small quantities are natural and commonly found in both indoor and outdoor air. In susceptible individuals, however, they may generate various allergic reactions [29]. Molds are the most common in summer, and from September to November the problem gradually decreases. The causes of heavy exacerbations of bronchial asthma in the late summer are seen in high concentrations of spores of the genus Alternaria and Cladosporium at this time (Figure 2 A,B). It is believed that fungi from the order of Mucorales and from Penicillium, Aspergillus or Trichoderma genus, may play a similar role [24]. The concentration of spores or conidia of certain fungi in indoor air may, however, be independent of the season. With this case we meet in the case of Serpula lacrymans, whose mature basidiocarps (Figure 3) release enormous amounts of basidiospores every day [30]. This fungus poses a threat not only because of the possibility of causing allergic reactions, but also because of the large amounts of various volatile organic compounds (VOCs) secreted during the active growth as well as at the time of death of its fruiting bodies. On the other hand, due to its strong cellulosic and lignolytic properties, this fungus is dangerous for building materials [31].
Figure 2: Alternaria alternata (Fr.) Keissl. [A] and Cladosporium cladosporioides (Fresen.) G.A. de Vries [B]-the most common etiological factors of different allergic reactions present in indoor air. Scale bar: [A] 30 μm and [B] 15 μm.
Figure 3: Mature basidiocarp of Serpula lacrymans (Wulfen) J. Schröt. Developed on wooden floor and released huge amounts of basidiospores every day. Scale bar 10 cm.
It has been shown that in the most cases the so called allergy to dust and seasonal hay fever are just the fungal spores, which are the main cause of these ailments. This is due to the fact that the fungal spores constitute a significant part of house dust [12,13]. Thus, an important reservoir of molds is home dust. The fungal flora present in the dust mostly reflects the airborne mycobiota of these rooms. With adequate humidity, the dust provides enough nutrients for fungi to grow. House dust usually consist large amount of organic matter and often have optimal pH for fungi [12]. Estimately, typical person inhales about 10 thousand liters of air per day. One liter of outdoor air that is considered clean often contains up to two dozen spores of fungi, bacterial cells, and a wide assortment of other small organic particles. Thus, the exposure of the respiratory system to numerous allergens is very high [32]. Mold-induced allergic reactions are often similar to those associated with influenza. It does not matter that some molds are classified as pathogenic and the others as non -pathogenic. Both groups are dangerous to human health [29]. As a rule, species of fungi that are typically pathogenic and cause mycoses are not allergenic [32]. The most common complaints associated with exposures to mold allergens are: runny nose, conjunctivitis, cough, upper respiratory tract congestion, chest pain or urticaria. Allergenic fungi can also enhance the symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis, in patients with allergic alveolar alveoli or with bronchial pneumonia (ABPA) [33].
FUNGI AS PRODUCERS OF VOLATILE COMPOUNDS
It is well known that fungi can secrete a lot of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which are one of many products of their primary or secondary metabolism [34,35]. The secretion of these chemical compounds is also directly related with a sick unit which is called sick building syndrome (SBS). Secretion of volatile substances as well as production of a huge amounts of extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) occurs especially when the molds grows in closed rooms, poorly ventilated with a high relative humidity [36]. It is well known that fungi exhibit greater metabolic activity under higher relative humidity [36,35]. The symptoms associated with secreted by fungi VOC the most often are manifested by lack of comfort, headaches, eye pain, pharyngitis, dry cough, dizziness, blurred vision, difficulty in concentration, sensitivity to smell, fatigue, apathy, or even a greater tendency to colds. These mainly neurotoxic symptoms are enhanced with a higher concentration of bioaerosol in indoor air [37]. It is characteristic that after leaving such a building or a room, these symptoms usually disappear quickly [38,39].
Such harmful conditions can exist only in one room, in the whole apartment or even in the whole building, especially if the latter has been built with inadequate materials to the typical climate in this region. The growth of fungi inside these spaces is always accompanied by the release of carbon dioxide and volatile organic compounds. Compounds secreted by fungi belong to such groups as aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons, alcohols, ketones, aldehydes or esters [40]. Among alcohols the most often are found 1-octanol, 2-octanol, methylbutanol or ethylhexanol. Apart from alcohols, terpenes and ketones are also often produced, such as 2-pentanone, 2-hexanone, 2-heptanone, 3-octanone, α-pinene, β-pinene, camphene, limonene, or methylfuranes. Among the aromatic hydrocarbons produced by fungi the most often are found cyclohexane and benzene [40].
The type of MVOC produced depends not only on the species of fungus but also on the nature of the substrate on which it grows. Moreover, differences exist also between strains from the same species. Often isolated and the most typical for indoor air fungi from the genus Aspergillus, Penicillium, Cladosporium and Fusarium are capable to produce a wide range of volatile compounds. It was showed that these species are able to secrete: formaldehyde, acrolein, nonanal, 2-pentanone, 2-hexanone, 2-heptanone, limonene, methylfuranes, camphene, or α-pinene [40]. It has also been shown that produced by many species of fungi formaldehyde and β-glucans shows strong irritation effect to mucosal membranes [41]. Not only fungi have the ability to produce MVOC. Such compounds can also be produced by bacteria and actinobacteria. Some compounds, such as monoterpenes, can also come from certain building materials, furniture, carpets and other sources [42].
MYCOTOXINS AS PRODUCTS OF SECONDARY METABOLISM
Showing the negative effects of fungi present in the direct human environment, it is impossible to ignore their toxic effects on the human body. With regard to human and animal health, the commonly known problem pose mycotoxins [43]. It is disturbing that among the fungal population there are observed virulent strains that have the potential for increased production of mycotoxins. This phenomenon may be related with the increasing use of plant protection products (pesticides, fungicides), of which the mutagenic effect is well known [44].
Mycotoxins are poisonous products of secondary metabolism of molds. It is believed that these compounds are needed by fungi in their natural environment, as most of these substances are produced against other microorganisms (including other species of fungi) as a manifestation of competition for ecological niches [45-47]. So far, more than 400 different mycotoxins have been described [48]. Mycotoxins can cause both acute and chronic disorders in humans [49]. To induce acute intoxication, which often ends with death, it is necessary to get a milligram dose per kilogram of body weight [48,49]. To poison by mycotoxins most often comes through ingestion of food contaminated with these compounds. However, taking into account the fact that mycotoxins can accumulate in different structures of mycelium and can diffuse into the culture medium the primary mycotoxicosis can occur even by inhalation of spores, conidia or fragments of mycelium. For example, Stachybotrys, chartarum produces mycotoxins which concentrated in conidia, phialides and conidiophores. A certain amount of these toxic compounds are also secreted into the medium, especially during the sporulation period. Another species, Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus produces mycotoxins which accumulate in conidia and sclerotia [50].
The significantly increased incidence of cancer in people inhabit moldy rooms in most cases is undoubtedly related with long-term exposure to mycotoxins [51,52]. Studies performed in Poland show that even a quarter of the dwellings are damp. From further calculations it seems that as many as 24% of the residents are at risk from mycotoxins and allergens secreted by fungi [15].
It is believed that tumor changes, especially cancer of liver or kidney, may be delayed effects of long -term exposition to low doses of mycotoxins of the human body [51,52]. Among the most important and the most commonly encountered in the environment mycotoxins are included aflatoxins, ochratoxin A, zearalenone, trichothecenes and fumonisins [48]. The first of the mentioned appears particularly dangerous to humans and animals because of their carcinogenic properties due to the benzofuran ring [53]. The most widely distributed in the environment producers of dangerous mycotoxins are numerous species of the genus Aspergillus. Many species from this genus, and in particular A. fumigatus, A. flavus, A. terreus, A. niger, A. clavatus and A. chevalierii were isolated from cellulose or collagen contained materials [54,55]. The mycotoxin production itself and the intensity of this process depend on the fungal strain, and its genotype. It also depends from its developmental stage, from the relative humidity and temperature, and from the chemical composition of the substrate, in which conditions that fungus grows. In the regard to the latter, the nature of the nitrogen source plays a particularly important role for the toxic compound production [48,53]. Mycotoxins are produced intensively at higher temperatures and under the higher relative humidity, and particularly inside the dwellings with poor ventilation [56]. For example, the optimal temperature for the formation of aflatoxin is 33oC. It has also been found that under the some levels of inorganic nitrogen, phosphates and under the conditions of oxygen depletion and elevated carbon dioxide the production of this toxin is inhibited [57].
It is especially important that most mycotoxins have affinity for certain organs and tissues. Kidney and liver-specific affinity for ochratoxin A seems particularly dangerous due to the prevalence of Aspergillus ochraceus in the environment. Equally dangerous are trichothecenes which appears to have gastrointestinal affinity and zearalenone which has a significant negative effect on the reproductive system [52,58-60].
In addition to the harmful effects of mycotoxins, allergens and volatile organic compounds produced by fungi, these organisms as pathogens can cause dangerous infections both superficial as subcutaneous or systemic. Only the genus of Aspergillus, which in the air of the dwellings occurs very often [61-64] contains dangerous pathogens. These include A fumigatus, A flavus, A terreus, A nidulans, A niger and A clavatus. The mentioned species as opportunistic pathogens especially in the case of predisposed individuals may be the cause of lung aspergillosis, keratitis or otitis [64]. As it was previously mentioned house dust may be an important reservoir of fungal spores or other propagules not only of mold but also of dermatophytes especially in homes with humidity problems. The presence of the latter is more likely in the flats where inhabitants have different domestic animals that leave the parts of the animal corneous epidermis or dander. This situation is conducive to the development of dermatophyte infections, whose etiological factors are zoophilic dermatophytes such as Microsporum canis (Figure 4) or Trichophyton mentagrophytes [12,65].
Figure 4: Micro and macroconidia of Microsporum canis E. Bodin ex Guég.-zoophilic dermatophyte whose natural reservoir may be home dust. Scale bar 10 μm.
Summarizing, with the presence of molds in dwellings always are connected some health problems, depending on individual sensitivity. The problem of the presence of fungi in flats and public buildings described in this article is becoming more real when we take into the considerations the fact that every day approximately every fourth Pole is exposed on fungal spores [15]. Spores of fungi and bacteria are ubiquitous in buildings and easily adapt to the niche available for them, as long as there is an adequate relative humidity and also a minimum amount of water available in the substrate. It should be underlined that the first ones are able to develop at significantly lower relative humidity levels as well as under the lower substrate humidity.
REFERENCES
- Nelson WC, Ott WR, Robinson JP. The national human activity pattern survey (NHAPS): use of nationwide activity data for human exposure assessment. Paper number 94-WA75A.01 presented at the A&WMA 87th Annual Meeting: Cincinnati, OH, 1994; and EPA Report, 600/A -94/147, AREAL: Research Triangle Park, 0-67, 1994.
- Wu F, Jacobs D, Mitchell C, Miller D, Karol MH. Improving Indoor Environmental Quality for Public Health: Impediments and Policy Recommendations. Environmental Health Perspectives. 2007; 115: 953-957. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Sh5Q6y
- World Health Organization. Indoor air pollutants: exposure and health effects. Report on WHO meeting. WHO Regional Office for Europe: EURO Reports and Studies. 1983; 78: 1-48.
- Marmot AF, Eley J, Stafford M. Building health: an epidemiological study of “sick building syndrome” in the Whitehall II study. Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 2006; 63: 283-289. Ref.: https://goo.gl/wVzvmU
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Indoor Air Facts No. 4 Sick Building Syndrome, Last updated on September 6, 2016, available at: https://www.epa.gov/indoor-air-quality-iaq/indoor-air-facts-no-4-sick-building-syndrome.
- World Health Organization. WHO guidelines for indoor air quality: dampness and mould. Edited by: Heseltine E and Rosen J, WHO Regional Office for Europe Scherfigsvej 8 DK-2100 Copenhagen O, Denmark 2009. ISBN 9789289041683
- Daisey JM, Angell WJ, Apte MG. Indoor air quality, ventilation and health symptoms in schools: an analysis of existing information. Indoor Air. 2003; 13: 53-64. Ref.: https://goo.gl/3dbOUs
- Laumbach RJ, Kipen HM. Bioaerosols and sick building syndrome: particles, inflammation, and allergy. Current Opinion in Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2005; 5: 135-139. Ref.: https://goo.gl/MQTRkT
- Joshi SM. The sick building syndrome. Indian Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 2008; 12: 61-64. Ref.: https://goo.gl/W9kL1I
- Bholah R, Subratty AH. Indoor biological contaminants and symptoms. International Journal ofEnvironmental Health Research. 2002; 12: 93-98. Ref.: https://goo.gl/GMwYnW
- Bloom E, Nyman E, Must A. Molds and mycotoxins in indoor environments-A survey in water-damaged buildings. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene. 2009; 6: 671-678. Ref.: https://goo.gl/8pKiV8
- Korpi A, Pasanen AL, Pasanen P. Microbial growth and metabolism in house dust”, w: International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation. 1997; 40: 19-27. Ref.: https://goo.gl/3uBSJO
- Adams RI, Tian Y, Taylor JW. Passive dust collectors for assessing airborne microbial material. Microbiome. 2015; 3: 46. Ref.: https://goo.gl/qkxwP9
- Takuma T, Okada K, Yamagata A. Mold colonization of fiberglass insulation of the air distribution system: effects on patients with hematological malignancies. Medical Mycology. 2011; 49: 150-156. Ref.: https://goo.gl/D6e0HO
- Zyska B. Fungi isolated from library materials: a review of the literature. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation. 1997; 40: 43-51. Ref.: https://goo.gl/VQnjDc
- Levy JI, Clougherty JE, Baxter LK, Houseman EA, Paciorek CJ, et al. Research report health effects institute2010; 152: 5-91. Ref.: https://goo.gl/o0LU98
- Sudakin DL. Toxigenic fungi in a water-damaged building: an intervention study. American Journal of Industrial Medicine. 1998; 34: 183-190. Ref.: https://goo.gl/uTYhQG
- Kuhn DM, Ghannoum MA. Indoor Mold, Toxigenic Fungi, and Stachybotrys chartarum: Infectious Disease Perspective. Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 2003; 16: 144-172. Ref.: https://goo.gl/jytLpj
- Tischer C, Chen CH, Heinrich J. Association between domestic mould and mould components and asthma and allergy in children: a systematic review. The European Respiratory Journal. 2011; 38: 812-824. Ref.: https://goo.gl/PafxZF
- Institute of Medicine (US) Vaccine Safety Committee; Stratton KR, Howe CJ, Johnston RB Jr, (editors) Adverse Events Associated with Childhood Vaccines: Evidence Bearing on Causality. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 1994; 4: Immunologic Reactions. Ref.: https://goo.gl/SX5x8D
- Marinkovich VA. Fungal hypersensitivity: pathophysiology, diagnosis, therapy. Advances in applied microbiology. 2004; 55: 289-307. Ref.: https://goo.gl/lDn6cM
- Horner WE, Helbling A, Salvaggio JE. Fungal allergens. Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 1995; 8: 161-179. Ref.: https://goo.gl/u9tk92
- Dick G. Immunological Aspects of Infectious Disease. Springer Science & Business Media, 2012; 245-249. ISBN 9401161917.
- Gupta M, Roshan R, Chhabra SK. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis without asthma complicating pulmonary tuberculosis. Lung India: Official Organ of Indian Chest Society. 2012; 29: 286-288. Ref.: https://goo.gl/MQu6rl
- Botterel F, Gross K, Ibrahim-Granet O. Phagocytosis of Aspergillus fumigatus conidia by primary nasal epithelial cells in vitro. BMC Microbiology. 2008; 8: 97. Ref.: https://goo.gl/5FV4xU
- Shah A, Panjabi C. Allergic aspergillosis of the respiratory tract. European Respiratory Review. 2014; 23: 8-29. Ref.: https://goo.gl/aGDb3t
- Bernatchez E, Gold MJ, Langlois A. Methanosphaera stadtmanae induces a type IV hypersensitivity response in a mouse model of airway inflammation. Physiological Reports. 2017; 5: e13163. Ref.: https://goo.gl/764QGk
- De Azevedo MI, Ferreiro L, Da Silva AS.Cholinesterase of rats experimentally infected by Cryptococcus neoformans: Relationship between inflammatory response and pathological findings. Pathology-Research and Practice. 2015; 211: 851-857. Ref.: https://goo.gl/NQPLSC
- Hardin BD, Kelman BJ, Saxon A. Adverse human health effects associated with molds in the indoor environment. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 2003; 45: 470-478. Ref.: https://goo.gl/cdnLWf
- Bryant DH, Rogers P. Allergic alveolitis due to wood-rot fungi. Allergy Proceedings. 1991; 12: 89-94. Ref.: https://goo.gl/QB71jI
- Pottier D. Airborne molds and mycotoxins in Serpula lacrymans-damaged homes. Atmospheric Pollution Research. 2014; 5: 325-334. Ref.: https://goo.gl/soiHa1
- Denning DW, Pashley C, Hartl D. Fungal allergy in asthma–state of the art and research needs. Clinical and Translational Allergy. 2014; 4: 14. Ref.: https://goo.gl/WPhzRZ
- Ansari S, Lotfi N, Hedayati MT. A review on the relationship between fungal allergens with allergy and respiratory diseases. Journal of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences. 2016; 25: 159-183. Ref.: https://goo.gl/d103YZ
- Morath SU, Hung R, Bennett JW. Fungal volatile organic compounds: A review with emphasis on their biotechnological potential. Fungal biology reviews. 2012; 26: 73-83. Ref.: https://goo.gl/SN8cvC
- Bennett JW, Inamdar AA. Are some fungal Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) mycotoxins? Toxins. 2015; 7: 3785-3804. Ref.: https://goo.gl/FUXgta
- Seppänen O, Kurnitski J. Moisture control and ventilation. In: WHO Guidelines for Indoor Air Quality: Dampness and Mould. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2009. Ref.: https://goo.gl/95yQah
- Fischer G, Dott W. Relevance of airborne fungi and their secondary metabolites for environmental, occupational and indoor hygiene. Archives of Microbiology. 2003; 179: 75-82. Ref.: https://goo.gl/JEKKur
- Terr AI. Sick Building Syndrome: is mould the cause? Medical Mycology. 2009; 47: 217-222. Ref.: https://goo.gl/FguAf9
- Borchers AT, Chang C, Gershwin EM. Mold and human health: a reality check. Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology. 2017; 52: 305-322. Ref.: https://goo.gl/vYFQFd
- Watson JG, Chow EM, Fujita EM. Review of volatile organic compound source apportionment by chemical mass balance. Atmospheric Environment. 2001; 35: 1567-1584.
- Pestka JJ, Yike I, Dearborn DG. Stachybotrys chartarum, trichothecene mycotoxins, and damp building-related illness: new insights into a public health enigma. Toxicological Sciences 2008; 104: 4-26. Ref.: https://goo.gl/CUYgB9
- Nurmatov UB, Tagiyeva N, Semple S, Devereux G, Sheikh A. Volatile organic compounds and risk of asthma and allergy: a systematic review. European Respiratory Review. 2015; 24: 92-101. Ref.: https://goo.gl/FWSKCL
- Tola M, Kebede B. Occurrence, importance and control of mycotoxins: A review. Cogent Food & Agriculture. 2016; 2: 1191103. Ref.: https://goo.gl/2SUGK3
- D’Mello JPF, Macdonald AMC, Postel D. Pesticide use and mycotoxin production in fusarium and aspergillus phytopathogens. European Journal of Plant Pathology. 1998; 104: 741-751. Ref.: https://goo.gl/R3nuHN
- Rosenzweig WD, Stotzky G. Influence of environmental factors on antagonism of fungi by bacteria in soil: clay minerals and pH. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 1979; 38: 1120-1126. Ref.: https://goo.gl/NSv8wX
- Prasad S, Manasa P, Buddhi S, Singh SM, Shivaji S. Antagonistic interaction networks among bacteria from a cold soil environment. FEMS Microbiology Ecology. 2011; 78: 376-385. Ref.: https://goo.gl/ezp44o
- Zapién-Campos R, Olmedo-Álvarez G, Santillán M. Antagonistic interactions are sufficient to explain self-assemblage of bacterial communities in a homogeneous environment: a computational modeling approach. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2015; 6: 489. Ref.: https://goo.gl/6XAdmi
- Bennett JW, Klich M. Mycotoxins. Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 2003; 16: 497-516. Ref.: https://goo.gl/1Tq8wg
- Hussein HS, Brasel JM. Toxicity, metabolism, and impact of mycotoxins on humans and animals. Toxicology. 2001; 167: 101-134. Ref.: https://goo.gl/x3U4pB
- Wicklow DT, Shotwell OL. Intrafungal distribution of aflatoxins among conidia and sclerotia of Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus. Canadian Journal of Microbiology. 1983; 29: 1-5. Ref.: https://goo.gl/nqrhjO
- Pitt JI. Toxigenic fungi and mycotoxins. British Medical Bulletin. 2000; 56: 184-192. Ref.: https://goo.gl/QbMSqM
- Nesic K, Ivanovic S, Nesic V. Fusarial toxins: secondary metabolites of fusarium fungi. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. 2014; 228: 101-120. Ref.: https://goo.gl/4gUA3r
- Mao J, He B, Zhang L. A structure identification and toxicity assessment of the degradation products of aflatoxin B1 in peanut oil under UV irradiation. Toxins(Basel). 2016; 8: 332. Ref.: https://goo.gl/O08yqh
- Krikstaponis A, Lugauskas A, Krysinska-Traczyk E, Prazmo Z, Dutkiewicz J. Enzymatic activities of aspergillus fumigatus strains isolated from the air at waste landfills. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine. 2001; 8: 227-234. Ref.: https://goo.gl/hEFTSG
- Rogerio-Candelera MS (eds.). Science, Technology and Cultural Heritage. 2014; 190-199, CRC Press, ISBN 1315712423.
- Khan HAA, Karuppayil MS. Fungal pollution of indoor environments and its management. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences. 2012; 19: 405-426. Ref.: https://goo.gl/a98mYo
- Milani JM. Ecological conditions affecting mycotoxin production in cereals: A review. Veterinarni Medicina. 2013; 58: 405-411. Ref.: https://goo.gl/WDvOUG
- Fink-Gremmels J, Malekinejad H. Review: Clinical effects and biochemical mechanisms associated with exposure to the mycoestrogen zearalenone. Animal Feed Science and Technology. 2007; 137: 326-341. Ref.: https://goo.gl/5e6WiI
- Wild CP, Gong YY. Mycotoxins and human disease: a largely ignored global health issue. Carcinogenesis. 2010; 31: 71-82. Ref.: https://goo.gl/eCdBcA
- Koszegi T, Poor M. Ochratoxin A: Molecular interactions, mechanisms of toxicity and prevention at the molecular level. Toxins. 2016; 8: 111. Ref.: https://goo.gl/s2B0pk
- Enoch DA, Ludlam HA, Brown NM. Invasive fungal infections: a review of epidemiology and management options. Journal of Medical Microbiology. 2006; 55: 809-818. Ref.: https://goo.gl/LKs6gV
- Segal BH. Aspergillosis. New England Journal of Medicine. 2009; 360: 1870-1884. Ref.: https://goo.gl/CPAapj
- Ho K, Cheng T. Common superficial fungal infections-a short review. Medical Bulletin. 2010; 15: 23-27. Ref.: https://goo.gl/rEytqu
- Brakhage AA. Systemic fungal infections caused by aspergillus species: epidemiology, infection process and virulence determinants. Current Drug Targets. 2005; 6: 875-886. Ref.: https://goo.gl/82R0x5
- Śpiewak R, Szostak W. Zoophilic and geophilic dermatophytoses among farmers and non-farmers in eastern Poland. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine. 2000; 7: 125-129. Ref.: https://goo.gl/TtKYpk
- Horvath EP, Anderson Jr H, Pierce WE, Hanrahan L, Wendlick JD. Effects of formaldehyde on the mucous membrane and lungs. A study of an industrial population. JAMA. 1988; 259: 701-707. Ref.: https://goo.gl/3OdLJj
- Keeney EL. Hypersensitivity to pathogenic and non-pathogenic fungi. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1950; 33: 418-430. Ref.: https://goo.gl/ImaKbS